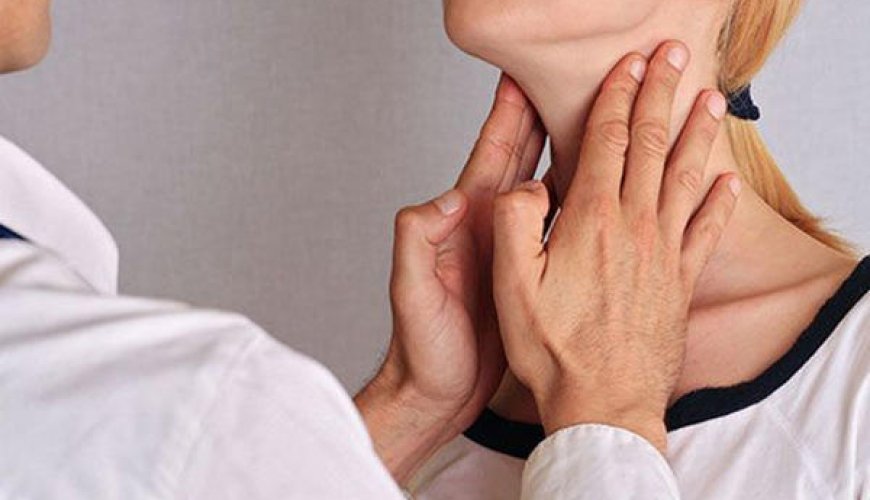
Goiter during pregnancy
To maintain the body's metabolism, thyroid hormones must be in a certain range in the blood. This normal range is called the euthyroid state. Hyperthyroidism is when thyroid hormones in the circulation are higher than normal values;
- Below normal values are called hypothyroidism.
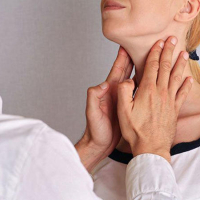
- An enlargement of the thyroid gland is known as a goiter.
- Goiter in pregnancy is popularly known as thyroid enlargement.
- An underactive thyroid can be caused by a lack of thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) or an overproduction of thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism).
Causes of goiter in pregnancy
During pregnancy, the thyroid gland can enlarge, so goiters can develop. Pregnancy-related goiter is more common in iodine-deficient regions of the world.
Symptoms of goiter in pregnancy
- Symptoms of goitre during pregnancy can be listed as follows;
- Irritation
- Heartbeat
- Constipation
- concentration problems
- Insomnia
- Sensitivity to cold and heat
- muscle cramps
Diagnosis of goitre in pregnancy
Pregnancy causes significant changes in thyroid function and thyroid gland shape. Therefore, thyroid test results in pregnant women show significant differences compared to non-pregnant women.
TSH and fT4 tests are used to evaluate thyroid functions during pregnancy. In this context, TSH target values that vary according to the week of pregnancy;
- 1st trimester 0.1-2.5 mU/L
- 2. trimester 0.2-3.0 mU/L
- 3rd trimester should be 0.3-3.0 mU/L.
Goitre treatment in pregnancy
In the first 3 months of pregnancy, the thyroid gland of the baby in the womb is not yet developed. The baby needs thyroid hormone for the development of the nervous system. During this period, the expectant mother's thyroid gland may work harder or grow to meet this need of the baby. In this process, it is important to adjust the medication under the doctor's supervision.
- Frequently asked questions about goiter during pregnancy
- Should all pregnant women have thyroid function tests?
- It is important for all mothers-to-be to have a thyroid function test during pregnancy.
- Since our country is an iodine deficiency region, thyroid dysfunction can progress with serious negative effects on the mother and baby
- Since TSH measurement has an acceptable cost for our country,
TSH measurement should be done at the beginning of all women and pregnant women. are planning a pregnancy.
Thyroid hormones are necessary for the normal development of the baby in the womb. Fetal thyroid gland 10-12 of pregnancy. It takes place on 18-20 of the week. begins to produce thyroid hormone. Therefore, the mother needs thyroid hormones for the development of the fetus in the first trimester. In cases where hypothyroidism is not properly treated;
- Down
- Preeclampsia (preeclampsia)
- low birth weight
- Premature birth
- It is important to detect and treat hypothyroidism in time, especially during the first weeks of pregnancy (first 8-10 weeks), when neuronal development takes place.
How is hypothyroidism treated during pregnancy?
Hypothyroidism is treated with thyroid hormone therapy in pregnant women and outside of pregnancy. Levothyroxine is a thyroid hormone drug that has an active ingredient. During the normal course of pregnancy, all pregnant women experience a 30-50% increase in thyroid hormone secretion. For this reason, the dose of thyroid hormone medication (LT4) should be increased, taking into account the increased need for thyroid hormone in mothers with hypothyroidism and already taking medication.
In pregnant women who were not known to have thyroid disease before pregnancy and hypothyroidism was detected for the first time during pregnancy, the main cause is first investigated, the need for medication and the level are determined.
The two most common causes of hypothyroidism in our country; autoimmune thyroid disease and iodine deficiency.
In the first 24 weeks of pregnancy, the frequency of monitoring is recommended to be every four weeks.
Thyroid hormone during pregnancy
- Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy can cause miscarriage, pregnancy-related hypertension, premature birth, anemia, arrhythmias, and in more advanced cases, heart failure and thyroid crisis.
- For this reason, it is important to plan treatment according to the underlying disease and, if necessary, to start antithyroid drugs and make appropriate dose adjustments.
- To decide how to treat hyperthyroidism during pregnancy, the cause of hyperthyroidism must first be known.
- The two most common causes are pregnancy-related transient hyperthyroidism and Graves' disease.
- Pregnancy-related hyperthyroidism is caused by an increase in beta HCG, is seen in the first 3 months, and usually goes away on its own and does not require treatment.
- However, in an autoimmune thyroid disease called Graves' disease, it may be necessary to use antithyroid drugs.
Due to the fact that there is a developmental anomaly in the baby related to one of the 2 antithyroid drugs used in our country, only the drug with the active ingredient propylthiouracil is used in the first trimester.
Thyroid surgery may be planned if thyroid hormone levels cannot be controlled with medication or if medication cannot be used due to side effects.
Diagnosis of thyroid cancer during pregnancy
If thyroid nodule cancer is diagnosed by biopsy in early pregnancy and the disease is limited to the thyroid gland, ultrasound examination is recommended for each trimester. Surgery early in pregnancy should be recommended in case of extrathyroidal spread and/or lymph nodes in the neck region. The operation is also performed in the second trimester.
Should pregnant women take iodine?
Daily iodine intake for pregnant women should be 250 µg/day. assuming that a pregnant woman consuming standard iodized salt has an average daily iodine intake of 100-150 µg/day, it is recommended that pregnant women take an iodine supplement of about 100 µg/day.