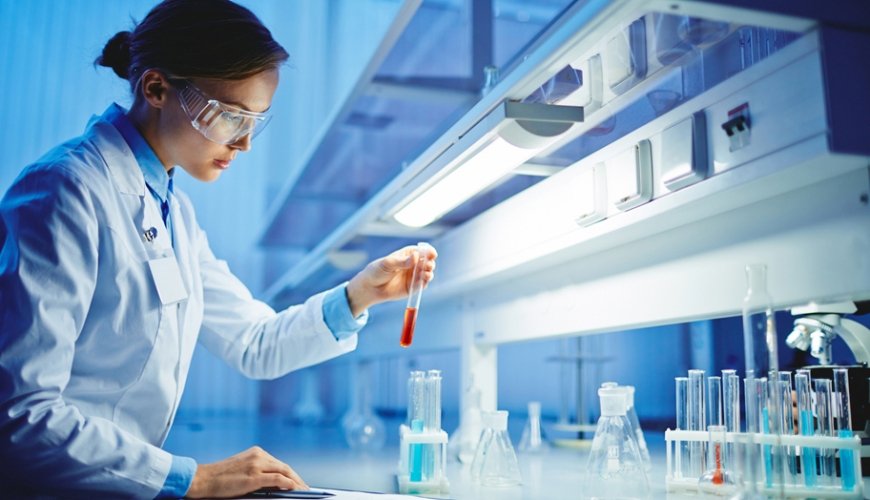
Medical Laboratory
- The Medical Laboratory Technicians department is one of the most interesting two-year departments in recent times.
- Students researching what the Medical Laboratory Technician department is, job opportunities, and curriculum, on the other hand,
- Medical Laboratory Technicians question the base and ceiling scores.
- Here all questions answers and base marks information related to Medical Laboratory Technicians section…
Medical Laboratory Techniques
- The purpose of the program is to train personnel who will conduct chemical analyzes in laboratories of clinical biochemistry, microbiology, pathology, molecular biology and genetics.
- Students studying in the Medical Laboratory Technician Program;
- He is studying intensively in basic medical sciences.
- As professional courses, biochemistry, microbiology, immunology, laboratory methods and calculations, pathology, genetics, hematology, endocrinology courses as well as anatomy, physiology, ethics, foreign language, Turkish language and Atatürk's principles are taught.
- Students are trained as individuals who are mentally and physically able to perform the given task at any time and under any conditions, strictly follow medical ethics and deontological rules, and respect the rights of patients.
The purpose of the Medical Laboratory Technicians Program is to train laboratory technicians who can perform medical analyzes deemed necessary by the doctor regarding the patient's condition in the diagnostic and treatment laboratories of health institutions. Graduates of this program have the knowledge and skills to perform biochemical, microbiological, pathological and hematological analysis of medical materials using laboratory equipment, machinery, instruments and equipment.
Biochemical analyses
Today, developing food technologies and consumer awareness increase the need to improve product quality. For this reason, ensuring food safety and quality control are of great importance in terms of consumer and public health
In this regard; In the Chemical Analysis Laboratory Unit, analyzes of food products, substances used in the production of food products, and drinking water samples required within the framework of import, export, special inquiries and inspections, and their witnesses are analyzed by methods valid at the national and international level.
In addition to the analysis of the main components of food, changes in the structure of food products during processing and storage, and various analyzes against fakes and forgeries are regularly performed in our laboratory.
The food sector is a constantly developing sector, and as a laboratory that follows the sector and scientific developments, our main goal is to increase the quality of analysis in accordance with the TS EN ISO / IEC 17025 standard by increasing the range of analyses. analyzes that cannot be done every year
- Major Research Topics
- Alcohol analysis
- Sugar Derivatives (HPLC)
- Drinking Water Analysis
- The composition of fatty acids
- Sterol content
- Search for vegetable oil
- Determination of cellulose
- Free fatty acid
- Polar Matter
- Determination of the amount of starch
- Caffeine
- Formol number etc.
Blood tests
- Blood tests are an important way to know the general condition of the body and get to the main problems without causing complications.
- These tests are also important to assess changes in physical health and reflect signs of aging over time.
- Important blood tests for adults are routine.
- They are also done before performing complex medical procedures.
- They serve as important markers to help your doctor assess health risks and plan further treatment.
But given that there are so many of them, it can be confusing which blood tests to do. We will discuss some important questions about blood tests and the most important blood tests for adults.
Blood test
- Many doctors will tell you to have a series of important blood tests every year or have them done during your general physical exam. However, if you have increased health concerns, it may be important for adults to have a series of important blood tests regularly. Important blood tests for adults help in the following cases:
- You already have conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels and other chronic diseases.
- You are obese, overweight or sedentary and want to focus on the consequences of an unhealthy lifestyle.
- You plan to check important parameters through laboratory values to monitor your health more closely.
- Important Blood Tests and Lab Values for Adults
These are some of the most important blood tests that are routinely recommended for adults. We also note the key lab values that accompany these tests to help you get a better idea of your test results
This test is one of the most commonly performed laboratory tests and one of the most important blood tests for adults. Complete blood counts monitor various parameters such as red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin level, and hematocrit (ratio of red blood cells to blood plasma). The test may be done for a variety of reasons, such as:
Diagnosis: Blood cell counts help doctors diagnose underlying conditions that may be affecting your health. If you can't describe your symptoms accurately or if you feel generally dull, your doctor may order a complete blood count and check various parameters for abnormalities.
Monitoring existing conditions: If you have existing conditions that cause abnormal blood counts, your doctor may recommend regular complete blood counts to check that treatment is working.
To Improve General Health: You may also receive doctor-ordered complete blood counts during regular physical exams to help monitor your health. It also prevents serious diseases by early detection of significant deviations in parameters.
The basic laboratory values for a complete blood test are:
- Red blood cells: Male - 4.32 - 5.72 million cells/mcL; Women - 3.90 - 5.03 million cells/mcL
- White blood cells: 3500 to 9600 cells/mcL
- Platelets: Men - 135,000 - 317,000 cells/mcL; Women 157,000 to 371,000 cells/mcL
- Hemoglobin: Men - 13.2 - 16.6 g/dL; Women - 11.6 - 15.6 g/dL
- Hematocrit: Men - 38.3% - 48.6%; Female - 35.5% - 44.9%
- Any significant deviation from these values may indicate vitamin and mineral deficiencies, anemia, systemic disorders, infections, cancer, or bone-related conditions.
Blood Sugar Tests
Blood sugar levels are important indicators of conditions such as type-1 and type-2 diabetes and gestational diabetes. Blood glucose tests should be included in all routine check-ups for middle-aged people and are important blood tests for adults in this age group. High blood sugar indicates that the pancreas is unable to produce insulin, that there is too little of it, or that the body's cells are resistant to the hormone. Insulin helps move glucose from the blood into the cells to be used as energy. However, diabetes causes high blood sugar levels and a lack of glucose in the cells. This results in various complications such as delayed wound healing, neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy and may even cause infections in the peripheral units. Blood glucose is measured before and after meals, during fasting and at random intervals during pregnancy.
- Fasting blood sugar: <100mg/dL
- Postprandial blood sugar: <180mg/dL
- Random blood sugar: <200mg/dL
- Any deviation above these values may indicate pre-diabetes or diabetes.
- Your doctor will recommend additional tests to confirm your diagnosis.
- If your blood sugar is below normal, you may have low blood sugar and your doctor will take special care of this condition.
Blood sugar
The test gives your doctor an idea of how the body works at the molecular level and helps pinpoint underlying causes of metabolic imbalances. Important laboratory values for this test:
- Sodium: 136-144 mEq/L
- Potassium: 3.7 - 5.2 mEq / L
- Chloride: 96 - 106 mmol/L
- Calcium: 8.5 - 10.2 mg/dL
- Blood Sugar: <100 mg/dL (fasting)
- Carbon dioxide: 23-29 mmol / L
- Blood urea nitrogen: 6 - 20 mg/dL
- Creatinine: 0.8 - 1.2 mg/dL
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): 44 - 147 IU / L
- Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT): 7-40 IU / L
- Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST): 10-34 IU/L
- Bilirubin: 0.3 to 1.9 mg/dL
- Albumin: 3.5 - 5.4 g/dL
- Total protein: 6 - 8.3 g/dL
Fluctuating values or abnormal values may require further investigation with more advanced tests. Skewed values can also indicate underlying chronic conditions or undiagnosed diseases. If you notice abnormal values on your metabolic panel, contact your doctor.